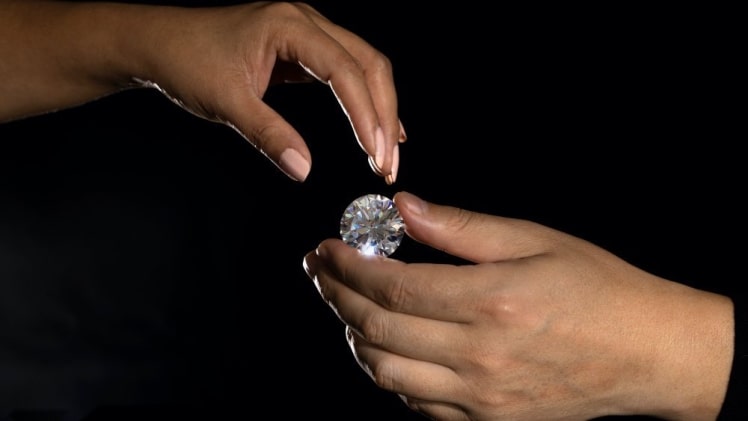
Lab diamonds vs real diamonds are real stones, similar to Natural Diamonds in chemical structure and visual characteristics. Despite the difference in size and shape, they sparkle just like Natural Diamonds. The key difference between natural and lab-grown diamonds is the way they are manufactured. A lab-grown diamond is produced in a controlled environment, with strict quality controls. However, these stones have different properties and are not as durable as Natural Diamonds.
Grown diamond
A lab-grown diamond is mass-produced by Chinese companies. In some instances, these stones can weigh over 10 carats when cut. In addition, the GIA has proven that the artificial stones have different patterns when they are analyzed using imaging instruments. The results of this study are not the same as the patterns in a natural diamond of the same clarity and color. Therefore, lab-grown diamonds are not the best choice for an engagement ring.
While a lab-grown diamond is cheaper than a natural diamond, it may not be the best option for an engagement ring. This type of stone is still a great option for a ring, but the price is often more expensive than natural diamonds. In addition, lab-grown diamonds are not as durable as natural diamonds. And since their supply is limited, the price will only rise in the future.
Natural
When comparing natural and lab-grown diamonds, it is important to keep in mind that a natural diamond is more expensive than a lab-grown one. This is because the latter is rarer and more valuable than natural diamonds. In addition, lab-grown diamonds are generally much lower in price, which means they are a cheaper option. The quality of both natural and lab-grown diamonds is the same, and the only differences are their karat weight and cut.
Lab-grown diamonds are similar to natural diamonds in terms of appearance, but the difference is not noticeable to the untrained eye. While they are similar in size, the difference between them is based on the amount of nitrogen that is present in the earth’s core. A natural diamond contains no nitrogen, so lab-grown diamonds are essentially equal. In addition to their low price, they are more sustainable and are a great option for a ring.
Lab diamonds
Although both natural and lab diamond vs natural are beautiful and durable, natural diamonds have a higher resale value. They will last longer and cost less, and are better suited for jewelry that requires high-quality cuts. Purchasing a natural diamond is the best option for engagement rings. Unlike lab-grown diamonds, the quality will not fade over time. They will always be more durable than a lab-grown diamond.
The quality of a lab-grown diamond is the same as that of a natural diamond. The chemical and physical properties of a natural diamond are the same. Its Mohs hardness rating is the highest of any gemstone. Nevertheless, a lab-grown diamond is vulnerable to chips, and it is important to protect them. Unlike natural diamonds, laboratory-grown diamonds are not a substitute for a real diamond. They have a lower Mohs hardness rating, but they are not inferior in quality.
Natural diamond improve
The cost of a lab-grown diamond is lower than a natural one, and the price of a natural diamond will be higher than that of a lab-grown one. The only difference between the two is the price. While a lab-grown diamond may be cheaper, it isn’t the best choice for engagement rings. Its value will continue to decrease as it gets older. The price of a lab-grown diamond will continue to decline and the quality of the diamond will not improve.All Movies Download From Jalshamoviez
In general
A lab-grown diamond looks like a natural diamond in terms of optical properties. However, the difference between a natural and a lab-grown diamond is not noticeable unless you look closely at it. This is why the two diamonds are similar in chemical and optical properties. They are equally durable. Buying a lab-grown jeweler-grown diamond is the best choice for the average consumer.