Introduction
This is an expanded article on fluoropolymer parts. See below for the full overview of this material.
Fluoropolymer components are used in a wide variety of products and applications, including:
Fiberglass or fiber reinforced plastic (FRP)
Polyvinyl chloride resins (PVC)
Polystyrene
Thermoplastic elastomers, such as low modulus polyacrylics, high modulus epoxy resins, and thermoplastic urethane.
Fluorelastomers
Fluoropolymers can be cured by various methods, which allow them to be made into very complex shapes. The following examples show how these materials can be prepared from other materials.
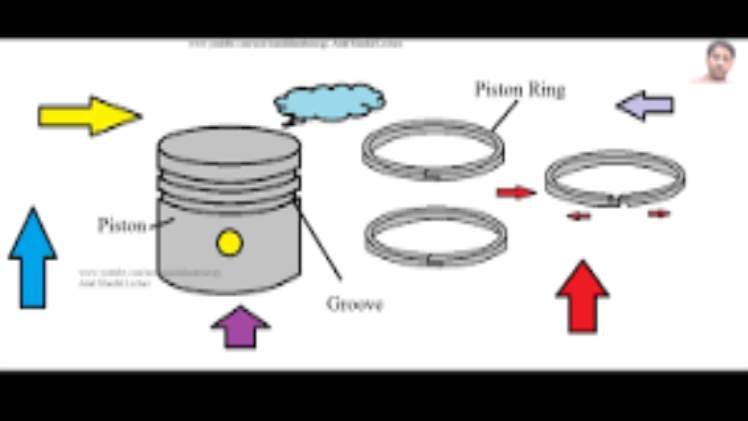
- PTFE Piston and Guide Rings for Dry Running Compress
- Chemical and thermal resistance to virtually all media used in hydraulics, pneumatics and technical gas applications
- Operating temperature range depending on application from -60°C to +200°C
- Suitable for use with no-hardened contact surfaces
- High bearing capacity, pressure resistance and low wear
- No stick-slip even with low sliding speeds and high transverse loads
Fluoropolymer composite, or PEEK
Fluoropolymer composites are often referred to as “PEK.” Many different processes can produce PEK and its variations, but they are typically produced with one of two additive manufacturing techniques: direct additive manufacturing or injection molding. In both cases, the polymer is made during the stage before it is placed onto the object it will serve in the final product.
Direct Additive Manufacturing (DAM): This process uses UV curing to build the shape of the 3D object. UV light irradiates the surface of a solid, creating a layer of photopolymerized resin and allowing for cross-linkable bonding between layers of the resin that holds the objects together. To achieve these bonds, ultraviolet lamps must pass through a series of filters that are deposited directly on the workpiece prior to exposure to the heat source to create a thin film of UV cure radiation. Once exposed to the UV lamp, the material in front of the machine emits ultraviolet rays and breaks down in preparation for use in the building.
Please Visit here For more idea about: Valerie Velardi
One important advantage of DAM is the fact that no separate processing steps occur during the manufacture process; instead, only UV light passes through the solid material, causing the entire structure to be cured using similar UV light. This results in a single continuous sheet of cured material. Another important benefit is the ease of cleaning since there is little residual interaction with the machine.
Injection Molding (IM): For many reasons, injection molding has become a popular alternative to DAM because it offers lower power consumption, greater efficiency, and does not require as much cooling of the equipment. However, there is still a higher risk of cross-linking during post exposure due to the proximity of the UV light source. One other significant drawback is that the production cycle is longer, which means a higher cost.
The Piston guide rings type KF prevents metal parts from contacting each other and additionally absorbs occurring shear forces. As standard, it is made of the compound PTFE + carbon or PTFE+ bronze; other materials are available. Given its good media resistance, the piston guide ring can be used in several media ranging from mineral oil-based hydraulic liquids, environment-friendly hydraulic liquids and water-oil emulsions to flame-resistant hydraulic liquids.
Piston guide rings offer very good gliding behavior, good emergency running properties and also a high wear resistance. Additionally, they help to attenuate mechanical vibrations.
Chemical and thermal resistance to virtually all media used in hydraulics, pneumatics and technical gas applications
Operating temperature range depending on application from -60°C to +200°C
Suitable for use with no-hardened contact surfaces
High bearing capacity, pressure resistance and low wear
No stick-slip even with low sliding speeds and high transverse loads
Fluoropolymer parts for plastics, composites, elastomers, thermosetting polymers
Fluoropolymer parts are manufactured through several methods, including thermal, chemical, and mechanical fusion (also known as vacuum deposition). Each of the techniques creates a variation to the original composition. The following table shows the main difference between each method.
This is another type of process where chemicals called precursors are added, and the resultant compound is cured. Depending on the chemistry involved, the resulting substance could be a polymer, a monomer, or an equivalent ester. Examples of precursors include ethylene glycol, vinyl chloride, benzene, and acetic acid. Some of the reactions employed during this type of process are transesterification, carbamide peroxide oxidation, sulfuric acid condensation, dehydration, and methanation. Solvent-based systems, such as hot solvent extraction and cold solvent extraction, may also occur in this process. Combustion or pyrolysis can occur in some systems or during pre-treatment. Processes involving the extraction of unwanted solids (i.e., water and insoluble organic solvents) can be done either with or without a catalyst. An example would be the distillation of the crude oil from diesel fuel. If it is the case that one of the pre-treatment steps is omitted, it is possible to perform an additional chemical reaction at the next stage, which should result in a polymer with fewer impurities (i.e., purer materials) ready for downstream synthesis or reprocessing. Finally, post-treatment steps may still retain some impurities. With regards to post-processing steps, such as depolymerization, washing, purification into isolation to remove impurities, and isolation, the presence of impurities may actually lead to better performance. Also, while post-processing in some cases cannot completely eliminate impurities, it can help improve some of their characteristics. Compounds of interest can sometimes contain traces of impurities that may be present since starting procedures in some cases can produce impure materials at the beginning of the system, and these impurities can increase as the system builds up and develops over time. Although some impurities are still present after the synthesis stage, the amount is usually negligible and cannot adversely affect performance. Post-processing is normally performed only if other steps have been conducted and the impure monomers have been isolated. Pre-treatment