G10 electrical materials are highly regarded in numerous industries owing to their exceptional properties and versatility. Understanding the G10 is crucial for various engineering and manufacturing endeavours, from their fundamental composition to diverse applications and evolving trends.G10 electrical materials, with their unique composition and properties, serve diverse industries and promise continued advancements in manufacturing and sustainability.
G10 Basics: An Overview
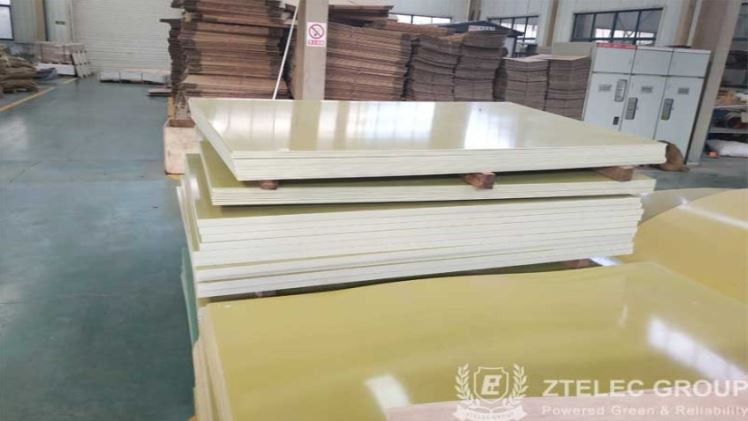
G10, a grade of Garolite, represents a composite material comprising layers of fibreglass cloth bonded with epoxy resin. This composite is renowned for its robustness, dimensional stability, and superb electrical insulation properties. Among its grades, G10 is the most prevalent choice across industries.
Properties and Composition
Composed of woven fiberglass infused with epoxy resin, G10 epoxy board undergoes curing under elevated pressure and temperature. This meticulous process results in a dense material boasting uniform mechanical traits. Noteworthy features include high tensile strength, minimal moisture absorption, and resistance to both heat and chemicals, rendering it suitable for demanding applications.
Applications and Uses
The versatility of G10 is expressed in its extensive utility across diverse sectors. It is a stalwart in electrical insulation, circuit boards, aerospace components, marine equipment, and sports gear. G10 is an insulating material for transformers, switchgear, and electrical enclosures, particularly in electrical applications, because of its outstanding dielectric properties and flame resistance.
Manufacturing Process Insights
G10’s manufacturing process entails layering fibreglass sheets with epoxy resin before subjecting them to heat and pressure in a hydraulic press. This meticulous procedure ensures optimal resin impregnation into the fibreglass, yielding a robust and homogenous material. Precision cutting and machining techniques then come into play, enabling the production of components with exacting tolerances.
Comparative Analysis: G10 vs. Alternatives
A comparative analysis between G10 and traditional materials like metal and plastic underscores G10’s superiority in several aspects. While metals may conduct electricity and plastics lack mechanical strength, G10 strikes a harmonious balance between these properties. Its higher strength-to-weight ratio, superior electrical insulation, and corrosion resistance render it an unparalleled choice across myriad applications. Moreover, in comparison to G11 material, G10 showcases similar properties while offering distinct advantages in terms of versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Maintenance and Durability Tips
Safeguarding G10 components mandate regular inspections for signs of wear, damage, or deterioration. Employing mild soap and water for cleaning helps rid the material of dirt and debris without jeopardizing its integrity. It’s imperative to avoid exposing G10 to excessive heat or harsh chemicals to ensure its longevity and durability.
Future Trends and Innovations
In tandem with technological advancements, the demand for lightweight, durable, and high-performance materials like G10 is poised to burgeon further. Innovations in composite manufacturing processes, including additive manufacturing and automated layup techniques, are poised to enhance cost-effectiveness and customization options. Furthermore, ongoing research into sustainable materials and recycling methodologies aims to mitigate the environmental footprint of G10 production and disposal.
G10: Versatile Innovations
G10 electrical materials epitomize a harmonious blend of superior mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties, rendering them indispensable across various industries. A comprehensive understanding of G10’s composition, properties, applications, and future trajectories is pivotal for unlocking its full potential in contemporary engineering and manufacturing landscapes.